响应式布局的几种典型方案
- 传统布局
- 相对单位布局
- 通过媒体查询实现
- 基于相对单位 rem 的 flexible 布局
- flex 布局
- grid 布局
1、传统布局
传统布局常见的是 圣杯布局 和 双飞翼布局 ,有以下特点
- 三栏布局,中间一栏最先加载和渲染
- 两侧内容固定,中间内容自适应
- 应用于 PC 端
1.1、圣杯布局
<div class="layout">
<div class="center col">center</div>
<div class="left col">left</div>
<div class="right col">right</div>
</div>
.layout{
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 1200px;
height: 600px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
margin: 20px auto;
padding: 0 250px 0 200px;
}
.col{
float: left;
}
.center{
background-color: blue;
width: 100%;
}
.left{
position: relative;
width: 200px;
background-color: pink;
margin-left: -100%;
right: 200px;
}
.right{
width: 250px;
background-color: pink;
margin-right: -250px;
}
1.1.2、疑难解惑
难点:为啥给
.right设置负的margin-right?
为方便理解,在
.right元素后,增加新的浮动元素<div class="col right1">right1</div>,
将
.right元素的margin-right设置成100px, 可看到.right1元素向左移动了100px, 这表明.right元素虽然显示宽度不变,但 实际所占的宽度 减少了 100px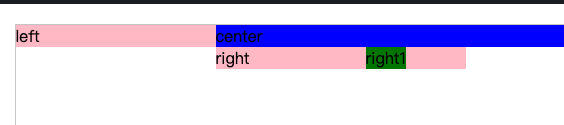
而当
.right元素的margin-right设置成-250px,虽然显示宽度还是不变,但 实际所占宽度为0 , 此时,.right元素自然不会被挤下来,而.right1元素也移动到了对左侧
在线DEMO: CSS 经典布局 - 圣杯布局
1.2、双飞翼布局
<div class="layout">
<div class="content-wrap col">
<div class="content">center</div>
</div>
<div class="left col">left</div>
<div class="right col">right</div>
</div>
.layout{
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 1200px;
height: 600px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
margin: 20px auto;
}
.col{
float: left;
}
.content-wrap{
background-color: #ccc;
width: 100%;
}
.content-wrap .content{
border: 1px solid #000;
margin: 0 250px 0 200px;
}
.left{
width: 200px;
background-color: pink;
margin-left: -100%;
}
.right{
width: 250px;
background-color: blue;
margin-left: -250px;
}
在线DEMO: CSS 金典布局 - 双飞翼布局
1.3、传统布局小结
- 使用
float布局 - 两侧使用
margin负值,以便和中间内容横向重叠 - 防止中间内容被两侧覆盖,一个使用
padding(圣), 一个用margin(双)
2、相对单位
CSS 中存在的相对单位有很多,但在使用过程中,需要考虑这些单位 到底是相对于谁?
2.1、em
相对与当前元素的字体宽度或当前元素继承来的字体的宽度。
“相对于谁” 取决于应用在什么 CSS 属性上。
- 对于
font-size而言,em是相对于父元素的字体大小; - 而在
line-height中,em是相对于自身的字体大小
2.2、rem
相对于根节点(html)的字体大小。
2.3、vw、vh、wmin、wmax
vw: 相对于视口宽度,一个视口宽度 =100vwvh: 同vwwmin:Math.min(1vw, 1vh)wmax:Math.max(1vw, 1vh)
2.4、%
2.5、calc()
响应式布局计算单位
3、通过媒体查询实现
通过 media query 设置不同屏幕下,根节点的 font-size 大小,页面中使用 rem, 从而实现响应式
缺陷:
media query和rem组合在屏幕尺寸上,是阶梯式的,并不能进一步的细分
4、flexible 布局
在 DOMContentLoaded, resize, pageshow 事件触发时,对 html 的font-size 值进行设定
font-size = document.documentElement.clientWidth / 3.75
在设计稿为 375px 时, html 的 font-size 值为 100, 也就是 1rem = 100px, 那么宽度是 75px 的元素,应该设计成 0.75rem
此时,当设备宽度是 414px 时,那么原先 75px 的元素应该自适应到 82.8px (75*414/375), 而写死的 0.75rem 不会改变,那么只需要将 html 中的字体设置为 104px (82.8 / 75) 即可
5、flex 布局
flexbox: 一种一维的布局模型,一次只能处理一个维度上的元素布局,一行或者一列
5.1、flex 中的轴线
- 主轴:由
flex-direction定义, 属性值可以是:row,row-reverse,column,column-reverse - 交叉轴:垂直于主轴
5.2、flex 容器
将容器的 display 属性设置成 flex 或 inline-flex, 其直系子元素会变成 flex元素
5.3、flex 元素
block layout:通过单通道算法(single-pass)进行布局的flex触发多通道算法(multi-pass code path)进行布局
ps: 单、多通道属于图形学知识